Peripheral artery disease treatment Perth
Peripheral artery disease: All your questions answered

Peripheral artery disease, or PAD, is a circulatory condition that may cause leg or foot pain. When plaque is building up in your arteries, it’s harder for your blood to carry nutrients and oxygen to the tissues in those areas. PAD may cause a stroke or heart attack so it’s important to manage it well when it’s been diagnosed.
How do I know if I have peripheral artery disease?
Your doctor may have said that you have peripheral artery disease, after you complained about leg pain when walking. However, many people don’t have symptoms at all and have PAD without knowing it.
They are at a higher risk for strokes and heart attacks, even though they don’t have symptoms.

Vascular Surgeon Perth
Adjunct Clinical Associate Professor at Curtin University
PAD can be medically and surgically treated, yet managing your lifestyle is an important first step. But before we dive into the treatment options for peripheral artery disease, let’s first explain what it is.
What is peripheral artery disease?
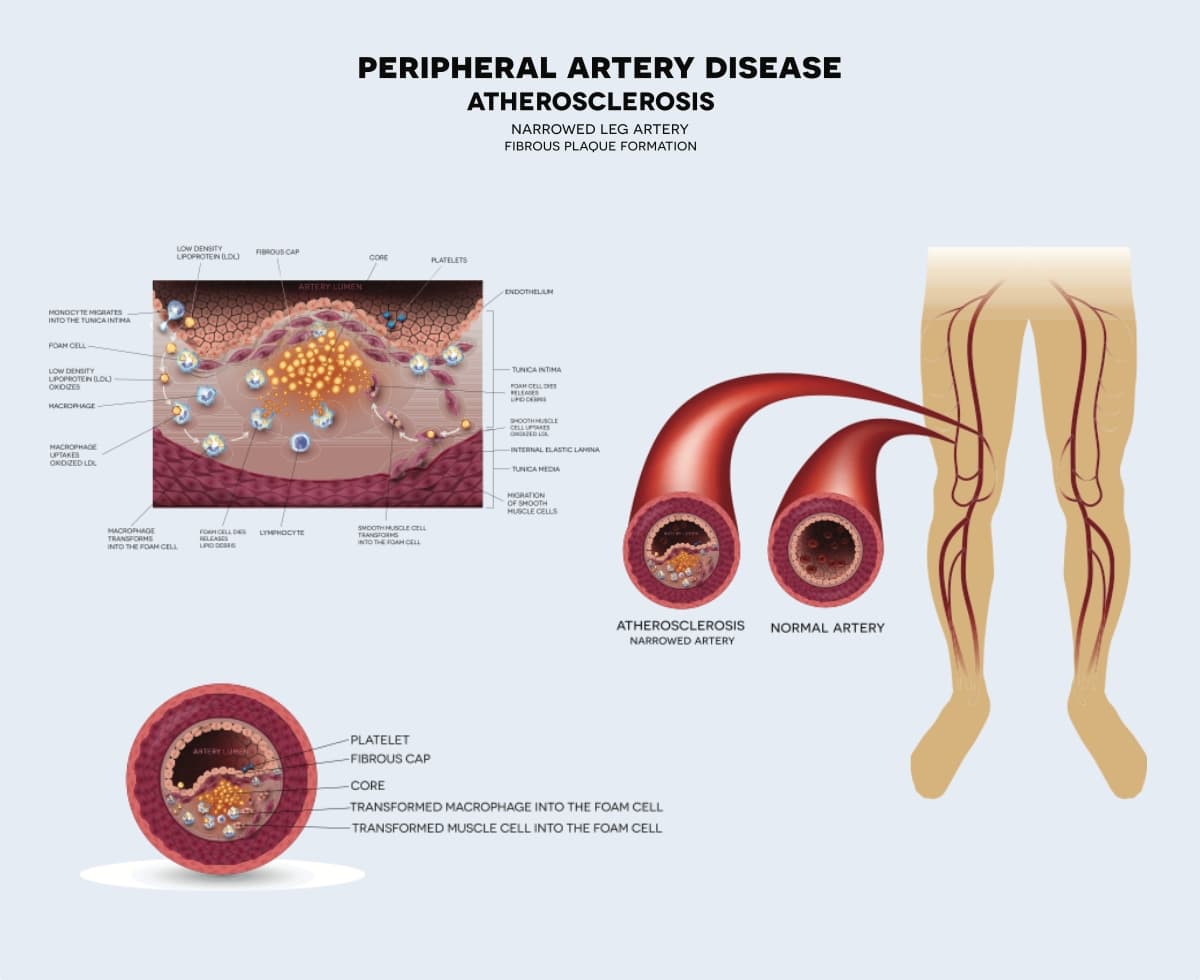
If you have peripheral arterial disease, fatty deposits (fats and cholesterol) are built up within the wall of the arteries of your legs. This is called atherosclerosis and it can cause your arteries to narrow, blocking your blood flow.
As atherosclerosis can affect different parts of the circulation, people with PAD commonly have atherosclerosis in other parts of the body as well. It means that if you have PAD, you are at an increased risk of strokes, heart attacks or kidney artery problems.
That is why PAD is a wake-up call; It identifies people who are at a higher risk of heart and brain problems.

Vascular surgeon Perth
Luckily, we can reduce your chances of having a heart attack or stroke by managing the risk factors.
What are the symptoms?
- Cramping in legs, usually in calves (claudication). This pain can be severe.
- Foot pain at night. This pain can be relieved by hanging your foot out of bed which may interfere with your sleep
- Cold feet/ legs
- Wounds on toes/ feet or legs that are very slow to heal
- Numb legs or feet
Tests that may be used to diagnose PAD include:
- Ankle Brachial Index (ABI): This simple test measures and compares the blood pressure in your ankle with your arm.
- Ultrasound: This test uses sound waves to assess how the blood flows within the blood vessels. It is a non-invasive test that is able to pick out blockages in the artery.
- CT scan: This test utilises X-ray waves to look at your blood flow within the blood vessels.
Can PAD be life-threatening?
The majority of people with PAD will have stable symptoms. In a minority of patients, PAD can be life-threatening.
- 5 years after diagnosis, about 5 to 10 out of 100 people can have blockages in the arteries that progress so much that they may get pain at night or sores in their feet. Some of those people may lose their leg (amputation) and could also die from it.
- 5 years after diagnosis about 1 in 5 people also may get a heart attack or stroke.
That’s why it is important to manage those risk factors that can cause heart attacks or strokes.
About 10-15 % of the Australian population have PAD (about 2-3 million people in Australia). It is common, but the majority of people will have no symptoms.
Risk factors for PAD and lifestyle choices
Smoking is the single most common risk factor to get peripheral artery disease.
Up to 4 out of 5 people who we diagnose with PAD are smokers or people who have smoked before.

Vascular and endovascular surgeon Perth
Other risk factors include:
- High blood pressure
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Age >60 years
- Having kidney disease
Making healthy lifestyle choices is an important part of managing PAD.
Stop smoking
Smoking damages the arteries and worsens PAD. If you continue to smoke after an operation to correct PAD, the outcomes are worse than if you stop smoking.
Exercise regularly
Exercise improves the way the body uses oxygen. Not only does it improve PAD, but it also reduces the chances of heart attacks and strokes.
Healthy diet
Eat a healthy diet and manage your weight.
Careful foot care
It is important to look after your feet, particularly if you have diabetes. Little injuries can cause small sores that may result in poor healing of those sores, particularly if the blood supply is reduced.
In addition, your doctor may give you medications to manage other risk factors. They may include
- A blood thinner, such as aspirin, which reduces the risk of heart attacks and strokes,
- Blood pressure tablets,
- Cholesterol-reducing tablets, such as statins.

What treatments are available for peripheral artery disease?
First of all, it’s important that you make those lifestyle changes as described above.
When you come and see me, I will explain to you that the treatment options depend on a range of factors. They include
- Severity of your symptoms,
- Where the disease is,
- The extent of the disease.
I will take a full history and examine you to map all the co-morbidities and decide what treatment is best for your case.

Vascular and endovascular surgeon Perth
Medical management
The choice of medical treatment depends on the presentation and your co-morbidities. You are likely to start on a blood thinner, something to control your cholesterol and blood pressure. Other risk factors that would be managed include
- Stop smoking,
- Lose weight,
- Exercise.
Peripheral endovascular management
Endovascular operations or ‘keyhole’ surgery are minimally invasive procedures used to open up blocked arteries of the legs or arms. A small tube is placed in the groin artery and dye is injected to identify the blockages in the arteries. Then the blockages can be treated by one or more of the following methods:
Angioplasty
Through the tube inserted in the groin, a balloon is advanced through the blockage. The balloon is then dilated to enlarge the narrowing of the artery sufficiently to improve blood flow.
Surgery, in the form of either ‘key-hole’ or open surgery, is able to treat the blockages within the blood vessels. However, the build of fatty deposits can still occur, particularly if you continue to smoke or if the risk factors are not managed.
After any surgery, you will need to be followed up by regular clinical exams and ultrasound scans to see if any further blockages appear.
Stent
Sometimes a stent will be placed in the artery to keep the artery open for the blood flow to continue. A stent is usually used in conjunction with a balloon to expand the stent.
Atherectomy
An atherectomy is a type of ‘drill’ that opens up very tight blockages in the vessel. This new device is usually used with balloon angioplasty or a stent to keep the vessel open.
Open surgical techniques
Sometimes the type and extent of the disease make endovascular treatment difficult. If this is the case, open surgery may be a better option. Open surgery requires hospital admission for several days and may require ICU admission.
Endarterectomy
An endarterectomy involves opening the artery surgically and removing the blockage physically. The artery is cleaned out and closed over with a patch (usually with a piece of the vein).
Surgical bypass
A bypass is used to improve the blood supply of the leg by using a graft (usually a vein from the leg or a plastic tube).
Frequently asked questions
Surgery, whether ‘key-hole’ or open surgery, is able to treat the blockages within the blood vessels. However, the build of fatty deposits can still occur, particularly if you continue to smoke or if the risk factors are not managed.
After any surgery, you will need to be followed up by regular clinical exams and ultrasound scans to see if any further blockages appear.
As with maintaining a healthy heart, you can maintain healthy leg circulation.
- Do not smoke
- Do regular exercise
- Eat a low-fat and low-sugar diet.
- Manage a healthy weight

About
Dr Altaf
As a vascular surgeon, I believe there is no one size fits all. This means appointments take as long until you fully understand the condition and are happy with my approach to get you the best treatment option.